第9節 - System.out.println()的用法和意思
這一節我會介紹一個Java的基本敘述(Statement) System.out.println(),這個敘述看似很簡單,但是其實背後是有很多學問。
我在第5節 - 用Eclipse寫Java程式示範過用System.out.println(),它主要用來把文字顯示在螢幕上。
例如: System.out.println("Hello, World!!");
Hello, World!!就會顯示在螢幕上。
System.out.println();的最好解釋(Best Description)
首先我會把我閱讀過System.out.println()最好的解釋記錄下來:
- This statement invokes the printlin() method of an object of the PrintStream class which is referred to (pointed to) by the variable named "out" which is a class variable of the "System"class.
- Out是java.lang.System的一個靜態欄位(類別變數),其型別為PrintStream類別,因此,println()是PrintStream類別的一個方法,System.out代表的是標準輸出,通常指的是螢幕。Println()之意為print與line,代表印出文字 並且換行。
- System is a final class in java.lang package. out is a static member field of System class and is of type PrintStream. Finally, println() is a method of PrintStream class.
- For a Class Field, we can either declare a Variable by Data Type or declare a Variable to Refer to an Object:
i) Declare a variable by data type, you can wirte:
e.g. int a=8;
This notifies the compiler that you will use "a" to refer to data whose type is "int". With a primitive variable, this declaration also reserves the proper amount of memory for the variable.
ii) You can also declare a reference variable:
e.g. Point originOne;
This uses Class "Point" to create a reference "originOne".
- When and where is the “out” instantiated in System.out.println()?
When the JVM is initialized, the method initializeSystemClass() is called that does exactly what it's name says – it initializes the System class and sets the out variable. TheinitializeSystemClass() method actually calls another method to set the out variable – this method is called setOut().
用Standard Java Naming Conventions去解釋System.out.println()
我在第8節 - Standard Java Naming Conventions解釋過,最主要原因是當大家用同一種方法(Standardization)去命名Java, Android和LibGDX時,當你學習其他人的程式編寫時,單單看程式碼,你就可以大約知道那一個是Class, Abstract, Interface, Variable, Method, Constant或Package,如下圖:
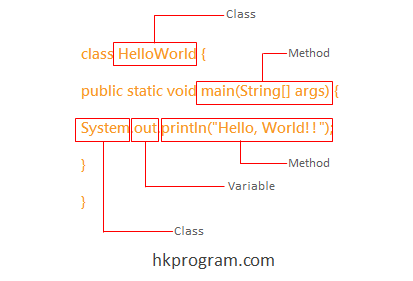
Helloworld是Classes類別
main()是Methods類別
System是Classes類別
out是Variables類別
println()是Methods類別
System.out.println()詳解
看完以上其他人的解釋和用Standard Java Naming Conventions去解釋System.out.println()後,想信大家會對System.out.println()有了初步了解,以下部分我會加以解釋:
首先System是一個Class,所以它是儲存在System.java檔案內,只要大家在Google Search "Java System.java",很容易就可以找到以下System.java的內容。
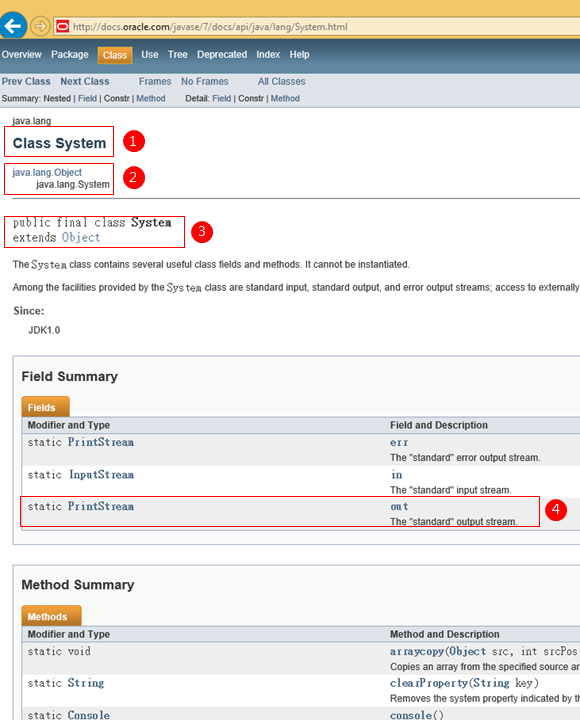
1-System 是一個Class。
2-System 是放在java.lang.System內。
3-System 是一個final class,如果一個Class定義為final,就代表這個Class不能被其他Class繼承(extends)。
4-System 的Field內,大家可以看到static PrintStream out;。
i) out是System的類別變數(Class variable),意思是大家可以用System.out而不可以用物件變數(Instance variable) e.g. system.out 是不可以的!
注意,我們假設Class"System"的物件是"system",大寫是Class; 小寫是Instance。
ii) Variable out也是PrintStream type。大家可以看到PrintStream是一個Class,所以它是儲存在PrintStream.java檔案內,只要大家在Google Search "Java PrintStream.java",很容易就可以找到以下PrintStream.java的內容。
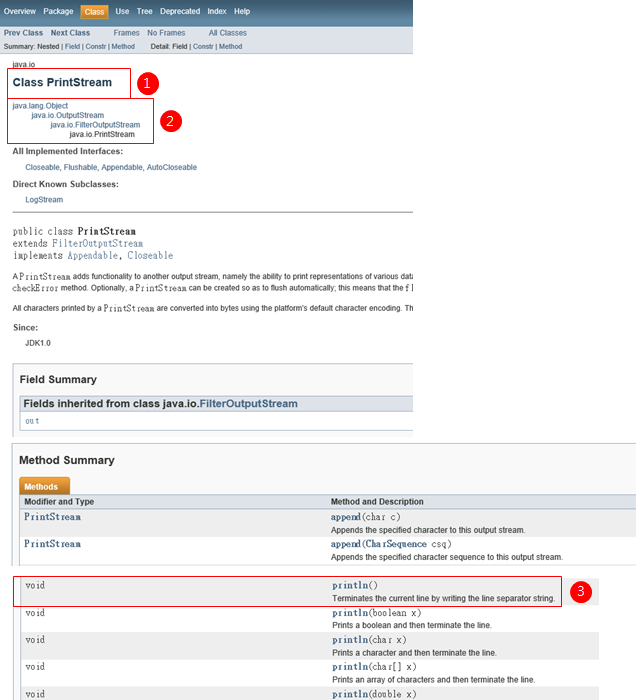
1-PrintStream是一個Class。
2-PrintStream是放在java.io.PrintStream內。
3-PrintStream的Method內,大家可以看到void println(); 今次大家可以看到println() Method沒有static println(),這代表println()是一個物件方法(Instance method),意思是大家可以用out.println()而不可以用類別方法(Class method) e.g. PrintStream.println() 是不可以的!。
注意,這次我們不須假設,Class "PrintStream"的物件真的是"out",大寫是Class; 小寫是Instance。
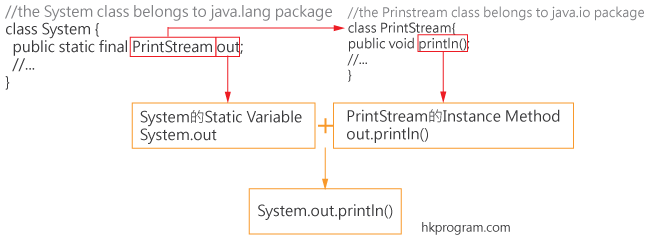
最後,把System的Static variable "System.out"和PrintStram的Instance Method" out.println()"合併,便變成System.out.println()。
最後用一個例子做示範作總結
首先用Eclipse建立以下程式:

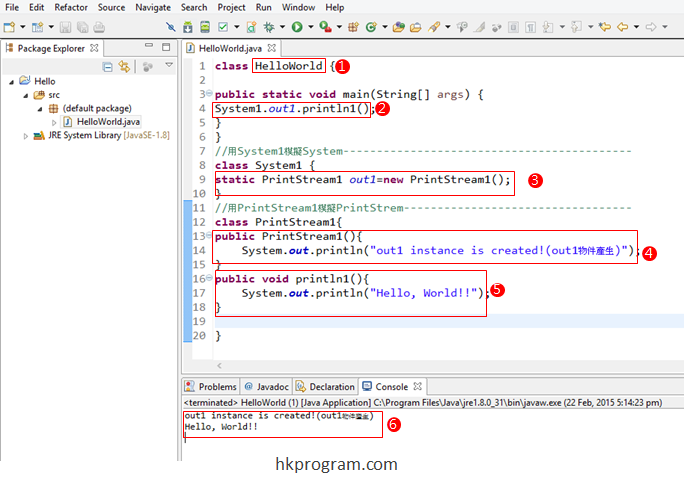
1-建立一個叫HelloWorld.java的程式。
2-在main() method內執行System1.out1.println1();。
3, 4和5-我們寫一個System1的Class模擬System Class。
再寫一個PrintStream1的Class模擬PrintStream Class。
最後寫一個out1的Variable模擬out。
注意static PrintStream1 out1=new PrintStream1()這一行; 這一行我們多了=new PrintStream1(); 這部分。因為out1只是PrintStream1的一個reference,PrintStream1的物件(instance)還沒有產生,必須用new去產生,所以就要建立PrintStream1的Constructor。
最後你可能會問為甚麼System內的PrintStream()只有static PrintStream() out;而沒有=new PrintStream();這部分,我在開始時介紹過以下的解釋:
5-When and where is the “out” instantiated in System.out.println()?
When the JVM is initialized, the method initializeSystemClass() is called that does exactly what it's name says – it initializes the System class and sets the out variable. TheinitializeSystemClass() method actually calls another method to set the out variable – this method is called setOut().
這是因為System Class (System.java)內有其他Method initializeSystemClass(),再呼叫另一個Method setOut()去產生一個物件(Instance)給out,所以不須要用new去產生一個物件。
System.java的內部程式不會在這裡詳細討論。